ISO 27001:2022 Requirements for Cybersecurity Training and Certification
In an era where data breaches and cyber threats have become commonplace, organizations are increasingly recognizing the need for robust cybersecurity frameworks. Among the multitude of standards available, ISO/IEC 27001:2022 stands out as a globally acknowledged framework for information security management. This standard not only addresses the management of information security risks but also emphasizes the crucial aspect of training and certification regarding cybersecurity. This article delves into the requirements of ISO 27001:2022 in the context of cybersecurity training and certification, providing insight into how organizations can safeguard their information assets.

Understanding ISO/IEC 27001:2022
ISO/IEC 27001:2022 is part of the ISO/IEC 27000 family of standards. It establishes a systematic approach to managing sensitive company information, ensuring its confidentiality, integrity, and availability. The key requirements revolve around establishing, implementing, maintaining, and continuously improving an Information Security Management System (ISMS). Among the various elements of an effective ISMS, trained personnel are essential to transform policies and procedures into actionable practices.
Key Requirements for Cybersecurity Training
The ISO 27001:2022 standard outlines several critical requirements related to training in cybersecurity. Here are the most notable ones:
- Identification of Information Security Roles
- Organizations must identify all roles related to information security within the framework of their ISMS.
- Each role should include a clear description of responsibilities and tasks associated with information security.
- Chief Information Security Officer (CISO): Responsible for leading the organization’s information security program, developing and implementing security policies, managing security incidents, and ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements.
- Information Security Manager: Responsible for overseeing the day-to-day operations of the information security program, including risk assessments, security awareness training, and monitoring security controls.
- Security Analyst: Responsible for identifying and analyzing security threats, monitoring security events, and responding to incidents.
- Network Security Engineer: Responsible for designing, implementing, and maintaining network security controls to protect the organization’s data and systems.
- Security Administrator: Responsible for managing user access, security configurations, and security tools such as firewalls and antivirus software.
- Incident Response Team: Responsible for responding to and investigating security incidents, coordinating with other roles to resolve incidents in a timely manner.
- Compliance Officer: Responsible for ensuring that the organization is compliant with relevant laws, regulations, and industry standards related to information security.
- Security Awareness Trainer: Responsible for educating employees about security best practices, policies, and procedures to help reduce the risk of security incidents.
- Data Protection Officer: Responsible for ensuring that the organization complies with data protection laws and regulations, including the handling of personal data and privacy concerns.
- Organizations must identify all roles related to information security within the framework of their ISMS.
- Competence and Awareness
- Organizations are obligated to ensure that personnel in key roles have the necessary competence to perform their tasks effectively.
- Training programs should be tailored to the specific needs of different roles, ensuring that employees understand how their work impacts information security.
- Organizations should also promote awareness of information security among all employees, not just those in key roles. This can be done through regular training sessions, communication campaigns, and reminders on the importance of following security protocols.
- Regular assessments of employee competence and awareness should be conducted to identify any gaps and address them accordingly. This may involve additional training, resources, or support to ensure that all employees are equipped to handle their responsibilities in a secure manner.
- By prioritizing competence and awareness within the organization, businesses can better protect their information assets and reduce the likelihood of security incidents or breaches.
- This proactive approach can also help foster a culture of security consciousness throughout the organization, leading to a stronger overall security posture.
- Organizations are obligated to ensure that personnel in key roles have the necessary competence to perform their tasks effectively.
- Ongoing Training and Education Programs
- Continuous professional development is vital in the ever-evolving landscape of cybersecurity threats.
- ISO 27001:2022 requires organizations to implement ongoing training programs and awareness campaigns to keep employees informed about current threats and best practices.
- These programs can include regular training sessions, workshops, webinars, online courses, and other educational resources.
- Employees should be educated on topics such as social engineering, phishing attacks, malware, ransomware, data breaches, and compliance requirements.
- Training should also cover topics like incident response procedures, reporting mechanisms, secure communication practices, password security, and data protection measures.
- Organizations should regularly assess the effectiveness of their training programs and make adjustments as needed to address new threats and vulnerabilities.
- By investing in ongoing training and education programs, organizations can help ensure that their employees are knowledgeable and prepared to protect against cybersecurity threats and safeguard sensitive information.
- Continuous professional development is vital in the ever-evolving landscape of cybersecurity threats.
- Evaluation of Training Effectiveness
- Organizations must assess the effectiveness of their training programs through methods such as feedback, testing, and performance evaluations.
- Regular reviews should be part of the process to ensure that training remains relevant and impactful.
- Training effectiveness can be evaluated through various methods, such as collecting feedback from trainees to understand their perception of the training program.
- Conducting assessments or tests to measure the knowledge gained by trainees can also help in evaluating the effectiveness of the training.
- Monitoring the performance of employees after the training can indicate whether the training has had a positive impact on their skills and capabilities.
- Regular reviews of the training program should be conducted to make any necessary improvements and ensure that the training remains relevant and beneficial to the organization.
- By systematically evaluating the effectiveness of training programs, organizations can ensure that their investment in training is yielding desired results and contributing to the overall success of the organization.
- Organizations must assess the effectiveness of their training programs through methods such as feedback, testing, and performance evaluations.
- Documented Evidence of Training
- Organizations should maintain documented evidence of all conducted training sessions and certifications obtained by employees.
- This documentation is critical for compliance audits and assessments.
- Training records should include details such as the date of training, the topics covered, the duration of the training, the trainers involved, and the number of employees who attended the training.
- Certifications obtained by employees should also be maintained, along with the expiration dates of these certifications to ensure that employees are up-to-date with their training.
- It is important for organizations to keep these records in a secure and easily accessible manner for audit purposes.
- Any changes or updates to training materials should also be documented to ensure that employees receive the most current information.
- Regular reviews of training documentation should be conducted to identify any gaps or areas for improvement in the training program.
- Organizations should maintain documented evidence of all conducted training sessions and certifications obtained by employees.
Implementing Cybersecurity Training Programs
Implementing effective cybersecurity training programs in accordance with ISO 27001:2022 involves several organized steps:
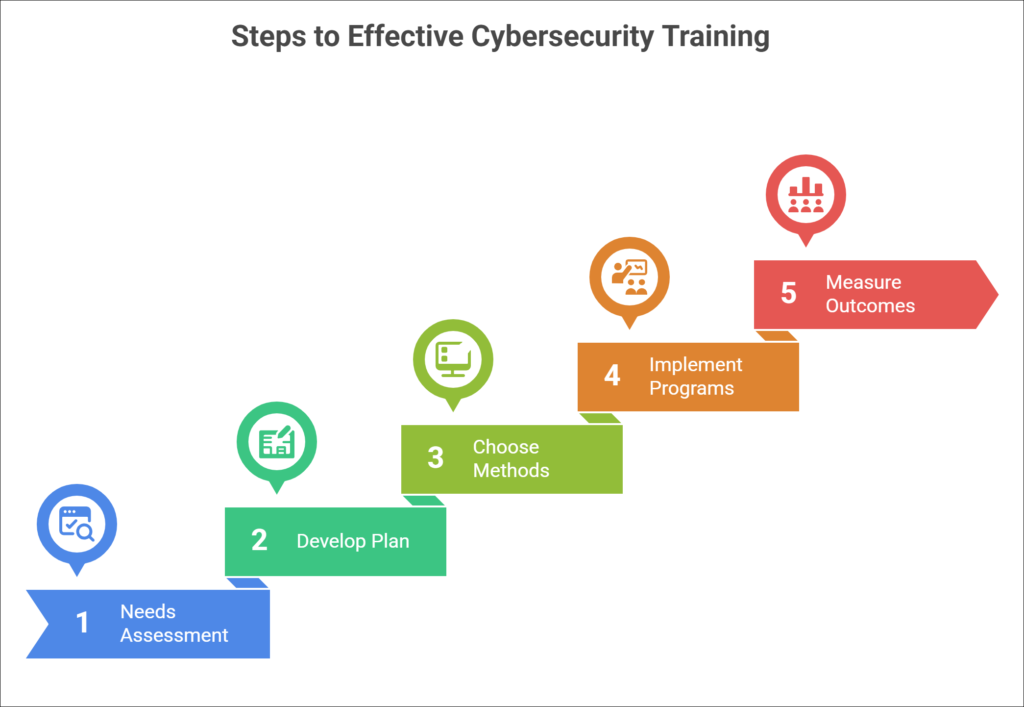
Step-by-Step Approach
- Conduct a Training Needs Assessment: Analyze the skills gap among employees related to cybersecurity practices.
- Develop a Training Plan: Collaborate with stakeholders to create a structured training plan that addresses specific needs identified during the assessment.
- Choose Delivery Methods: Depending on the audience, training can be delivered through various methods such as online courses, workshops, or seminars.
- Implement Security Awareness Programs: These should highlight current threats, company policies, and procedures, promoting a culture of security.
- Measure Outcomes: Utilize metrics to evaluate the success of training initiatives, including pre- and post-training assessments and employee feedback.
Certification Standards
Obtaining certification under ISO/IEC 27001:2022 is not just about compliance; it signifies that an organization has taken significant steps toward establishing a mature information security management system. Certifications can be done by various accredited bodies, and the process generally involves:
- Pre-Audit Assessment: A preliminary review to identify areas needing improvement before the formal audit.
- Formal Audit: An in-depth examination of the ISMS by an external auditor, verifying compliance with the standard.
- Certification Issuance: Once compliance is confirmed, the organization receives a certification confirming its adherence to ISO 27001:2022 standards.
- Surveillance Audits: Post-certification, periodic audits are necessary to ensure ongoing compliance and address any emerging risks.
Conclusion
ISO/IEC 27001:2022 sets a comprehensive framework for cybersecurity training and certification that is essential for organizations looking to fortify their information security posture. By incorporating structured training programs and obtaining certification, businesses can not only enhance their defensive measures against cyber threats but also build trust with clients and stakeholders. In this fast-changing digital world, investing in robust cybersecurity training is no longer a luxury but a necessity that every organization must embrace. By prioritizing these practices, organizations position themselves effectively to navigate the complexities and challenges of today’s cybersecurity landscape.
